
Eczema/Itchy Skin
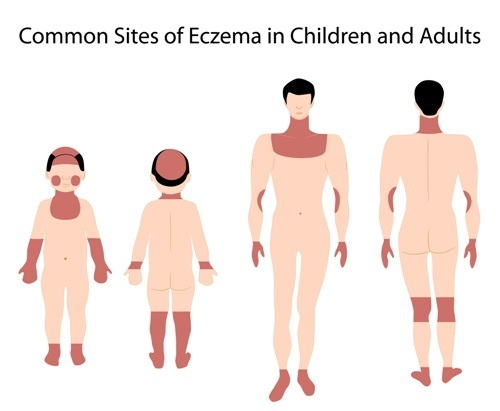
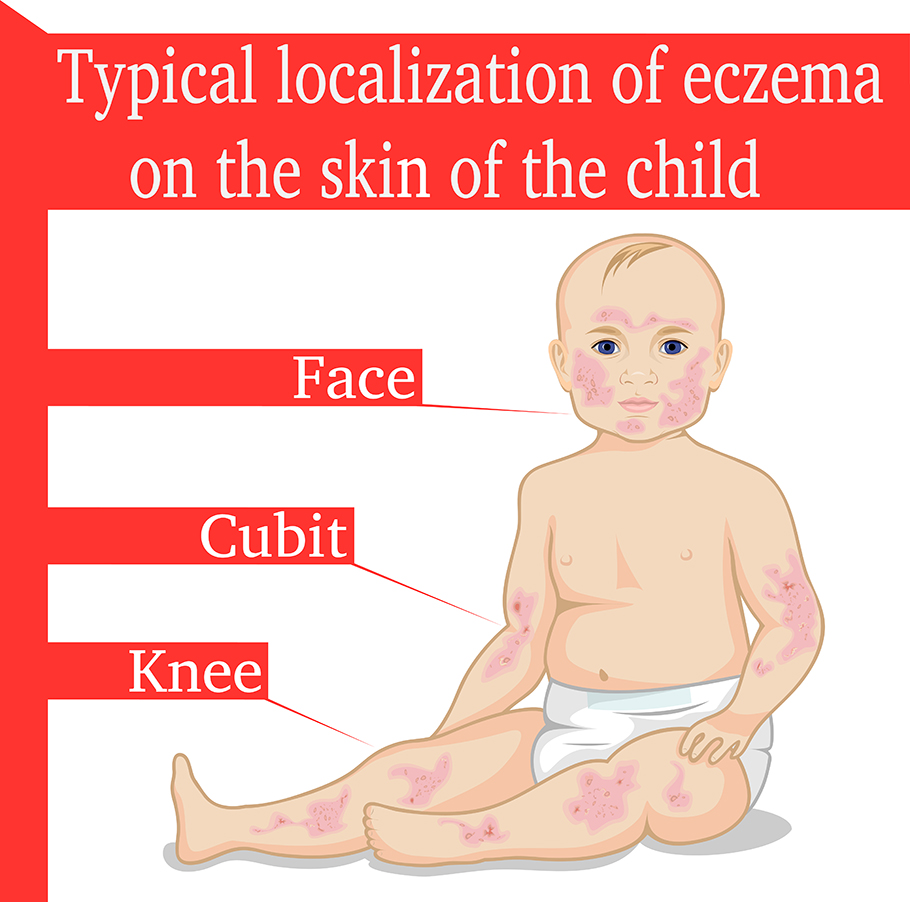
Eczema is a general term for a variety of inflamed skin conditions, one of the most common of which is atopic dermatitis.
Many skin rashes can appear like eczema, it is not best to assume it is and is often best to consult with your dermatologist for assessment and further management.
ATOPIC DERMATITIS (ECZEMA)
Atopic Dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that recurs, with intermittent episodes of inflamed skin.
It is believed that Atopic Dermatitis is due to the interplay of multiple factors including environmental factors and inherited factors which combine to create an abnormal immune / inflammatory response in the skin.
While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, various triggers have been identified including hot, humid or dry environments, foods and even certain coarse fabrics. These triggers vary from person to person.
In general Atopic Dermatitis can be managed but it cannot be cured.
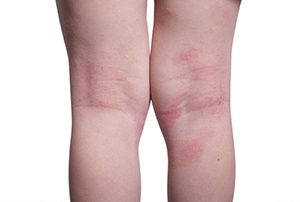
Atopic Dermatitis is often characterised by regions of itchy, red, dry patches on the skin. Normally it occurs on the backs of the knees, front of the elbows and neck, however in more severe disease it can occur anywhere on the skin.
Since eczema is sensitive to certain triggers, part of the dermatologist’s care will be education as to how an individual can avoid them.
Eczema is a common childhood skin rash. In addition to occurring on the back of the knees, front of the elbows and neck, it can also occur on the hands, feet and the face.
ECZEMA MANAGEMENT

IDENTIFY TRIGGERS AND AVOID THESE
This may include clothing , change in temperature , sweat , foods etc.
IMPROVE SKIN BARRIER FUNCTION
Improve the barrier function with moisturisers tailored to the circumstances and the person.
REDUCE BACTERIA AND CONTROL INFECTION
A high percentage of people with eczema carry bacteria that can lead to secondary infection of eczema. This bacteria also may trigger eczema.
Treatment of secondary infection and measures to reduce certain bacterial on the skin may improve eczema control.
Bleach baths are an effective method for reducing bacteria loads on the skin and may be used bu your Dermatologist as part of your management plan.
BLEACH BATH RECIPE
USE TOPICAL STEROIDS WHEN THE SKIN IS INFLAMED
If inflammation (redness and itch) are present topical steroids are essential to treat eczema. These are very safe if used appropriately.
Safety of topical steroids
 reference
reference
- Mooney E et al. Adverse effects of topical corticosteroids in paediatric eczema: Australasian consensus statement. Australas J Dermatol. 2015 Mar 6. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12313.
Your dermatologist will work with you to maks a plan to treat your eczema during flare ups and to maintain control. These plans are customised to suit the individual.
PHOTOTHERAPY (LIGHT THERAPY) FOR ECZEMA
 Narrow Band Ultraviolet B therapy can be used to treat eczema.
Narrow Band Ultraviolet B therapy can be used to treat eczema.
Phototherapy / UVB helps to calm inflammation leading to reduced itch.
It is often used in conjunction with other treatments to control widespread eczema.
The treatment involves a short attendance at the clinic for treatment 2-3 times per week.
The treatment takes as little as 30sec to a few minutes each attendance.
A typical treatment duration is 6 -12 weeks
UVB treatment (whole body and hand /foot) is available at our Stafford rooms and is bulk billed.
ECZEMA ASSOCIATION PHOTOTHERAPY GUIDE



